Version note: This will only work in the latest dev build of QGIS – not in 1.8
The lack of uni for the next couple of weeks has left me some time at night to work on some features that I really wish QGIS had. One of these features was better date and time support in the expression engine. Date and time is an important concept when working on inspection data and not being able to style my features in QGIS using date operations was bugging me. So in good open source fashion I added some.
Here are the current functions (more to come in the future):
- $now – returns the current date and time
- age({datetime},{datetime}) - returns the difference between the two dates
- todate({string}) - converts a string to date type
- totime({string}) – converts a string to time type
- tointerval({string}) – converts a string to a interval type (details below)
- day({datetime} or {interval}) – returns the day from a datetime type or the number of days in a interval.
- hour(…) – Same as above but for hours
- minute(…) - Same as above but for minutes
- second(…) - Same as above but for seconds
- day(..) - Same as above but for days
- week(..) - Same as above but for weeks
- month(…) - Same as above but for months
- year(…) - Same as above but for years
- {datetime} – {interval} = {new datetime} – returns a new datetime subtracting the interval
- {datetime} + {interval} = {new datetime} – returns a new datetime adding the interval
The interval type
Functions like age(..), tointerval(), {datetime} -/+ {interval}, day(..), hour(..), etc, use, or return, Intervals. An Interval is a measure of time that we can use for different things. An example of an Interval is ’1 Year 2 Months’ this is then converted to a number of seconds and used for any calculations.
For example one can take away 10 days from the current date by doing the following ( -> marks the output ):
todate($now - '10 Days')
-> 2012-06-20
as
todate($now)
-> 2012-06-30
We can also do something like:
todate($now + '2 Years 1 Month 10 Days')
-> 2014-08-10
The age() function will return an interval which we can use extract what information we need.
The number of days between two dates:
day(age('2012-06-30', '2012-06-10'))
-> 20
-- Think of it as '2012-06-30' - '2012-06-10'
-- Note: day(), month(), etc, functions return doubles so you can get
-- 21.135234 days if you are using date & time type rather than just date type
-- wrap the result in toint() to get a more sane output.
Day() will also work on a plain date:
day('2012-06-30')
-> 30
We can even get the number of seconds between two dates:
second(age('2012-06-30', '2012-06-10'))
-> 1728000
Currently the only date format supported is {year}-{month}-{day} as seen in the examples above. Shouldn’t be too hard to add support to the todate(), todatetime(), totime() functions for giving it a pattern to use when converting the string e.g. dd-mm-YYYY, or something like that.
More on this fancy new stuff
When I wrote the new expression builder dialog a while ago I made it dynamic so that any new functions added to the expression engine will show up automatically. So here they are:

List of new date and time functions.
We can also use these functions in the rule based rending, which is where the power really comes in. Lets see something like that in action:

Styled using days and years
Should be pretty straight forward to understand. We are using the age() and day() functions to style the events that are older than 30 days, within 30 days, for today, or in the future. We also check the year of the event using year() and year($now) to make sure we only see this years events, or style them differently depending on if they are last years events or in the future.
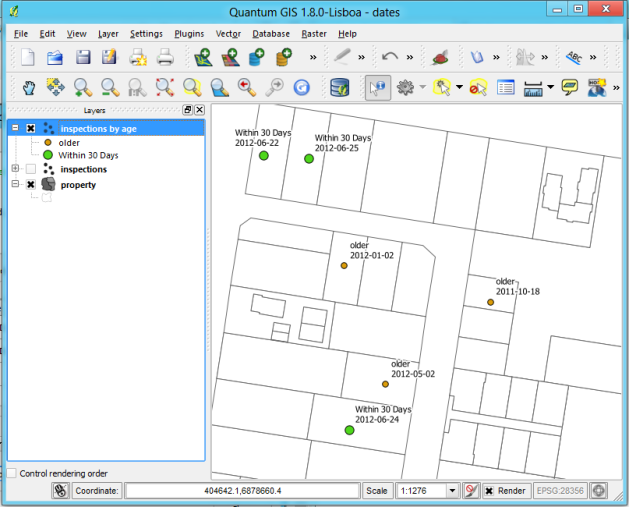
This is the result of the above rules:

Result of using date functions in rule based renderer
I’m also using the date functions in the expression based labelling to label the features using the following expression:
CASE
WHEN year( "dateadded") < year($now) THEN
'Last Year'
WHEN day(age("dateadded", $now)) < 0 THEN
day(age("dateadded", todate($now))) || ' Days old'
ELSE
day(age("dateadded", todate($now))) || ' Days to go'
END
Well that’s it. Hope you find it handy in your day-to-day mapping. I know I will be using it a lot.
Thanks to Martin and Jürgen for the code reviews during the process; venturing in an unknown part of the code base always makes me nervous but that is all part of learning, and sometimes you can make some pretty cool stuff.
Some other random notes: The general idea has been modelled of how Postgres handles dates and times, it’s not an exact copy but follows the same kind of ideas. The interval class also uses the same number of seconds for one year that postgres does so that we can be consistent with the output.
Filed under:
Open Source,
qgis Tagged:
FOSSGIS,
gis,
map-rendering,
Open Source,
osgeo,
qgis,
Quantum GIS,
styling